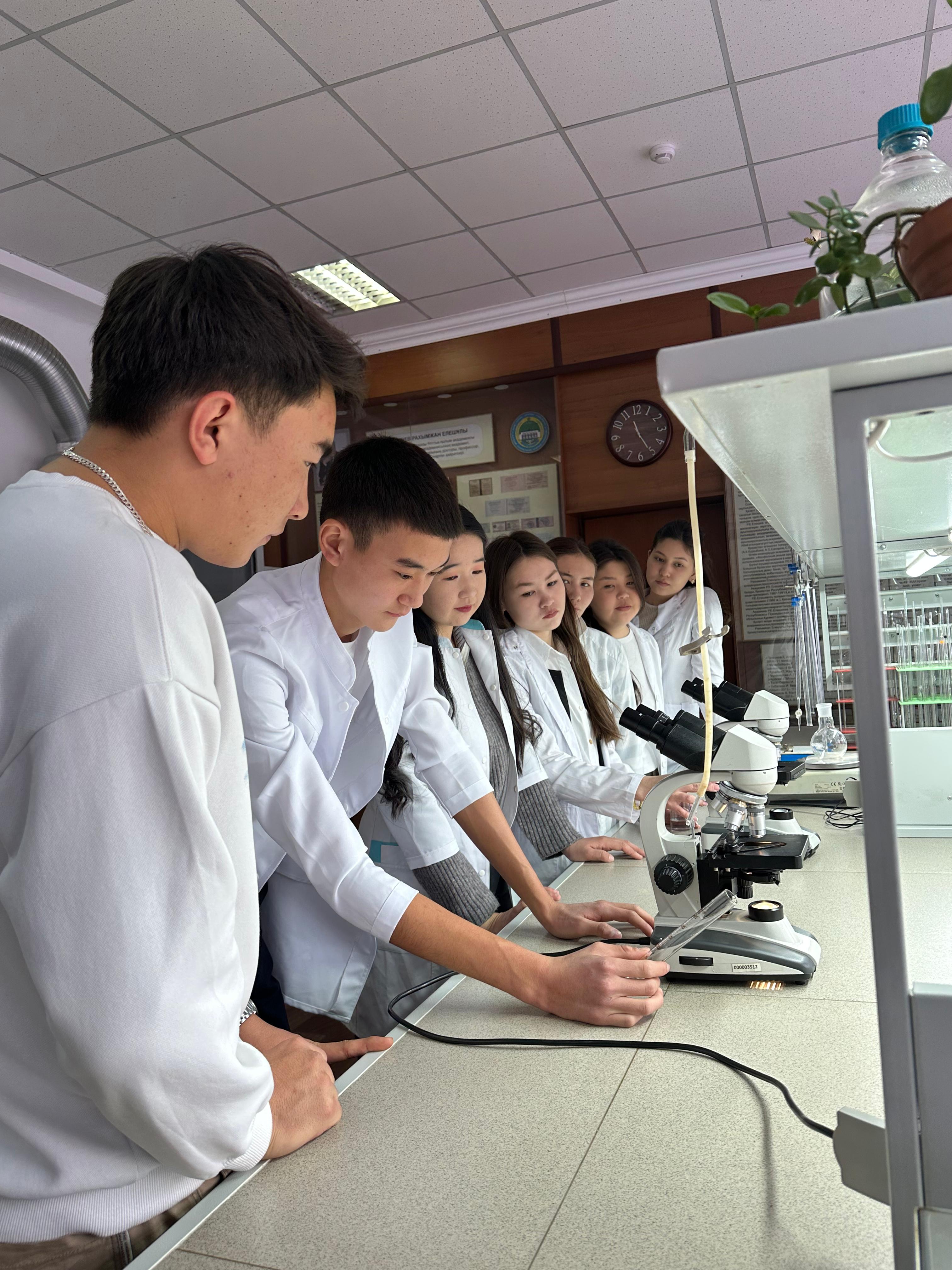
- агроном-агрохимик
- агроном-топырақтанушы
- тұқым шаруашылығы бойынша агроном
- өсімдіктерді қорғау агрономы
- инженер-эколог
- аудан, облыс, республика ауқымында агрохимиялық қызмет және топырақ-іздестіру жұмыстарын ұйымдастыру;
- тұқым және отырғызу материалдарының энтофито-патологиялық жай-күйін бақылау және егістіктерді зерттеу.
- ауыл шаруашылығындағы жер ресурстары;
- егуге рұқсат етілген ауыл шаруашылығы дақылдары, ауыл шаруашылығы дақылдарының сорттары мен будандары;
- егіс алқаптарын аурулардың болуына диагностикалау және зиянкестермен күресуге және алдын алуға бағытталған алқаптарды өңдеу бойынша агротехникалық жұмыстарды жүргізуге дайындау.
- биохимиялық бақылау әдістерін қолдана отырып, өсімдіктерді аурулардан, зиянкестерден қорғау бойынша агротехникалық жұмыстар жүргізу.
- тозған жерлерді жемшөп дақылдарын өсіруге дайындау
- тозған жерлердегі ауыл шаруашылығы жұмыстарын басқару
- акционерлік қоғамдар, өндірістік кооперативтер, жауапкершілігі шектеулі серіктестіктер, ауыл шаруашылығы бағытындағы фирмалар;
- фермерлік, шаруа қожалықтары және өндірістік кооперативтер;
- ауыл шаруашылығы саласындағы эксперименттік-зерттеу мекемелері;
- өсімдік шаруашылығы өнімдерін сақтау және қайта өңдеу кәсіпорындары;
- өсімдіктерді қорғау және карантин жөніндегі мекемелер;
- агрохимиялық қызмет мекемелері;
- ауылшаруашылық тәжірибе станциялары.
- ауыл шаруашылығы бағытындағы ғылыми-зерттеу институттары мен жоғары оқу орындары.
- фермерлік және шаруа қожалықтары, жеке өндірістік кооперативтер, акционерлік қоғамдар, жауапкершілігі шектеулі серіктестіктер, агроөнеркәсіптік кешендер, білім беру ұйымдары, бейінді ғылыми-зерттеу институттары мен орталықтары және т. б.;
- ауыл шаруашылығы дақылдарын өсірудің технологиялық карталарына сәйкес өсімдік шаруашылығы бригадаларының жұмысын ұйымдастыру;
- топырақ құнарлылығын молайту және оны эрозиядан қорғау жөніндегі агротехникалық іс-шаралар жүйесін жоспарлау, ұйымдастыру және іске асыру, өрістердің оңтайлы фитосанитариялық жай-күйін құру;
- жаңа технологиялар мен сорттарды қолдану бойынша тәжірибелік жұмыс жүргізу;
- вегетация кезеңінде өсімдіктердің даму процесін бақылау;
- гербицидтерді, фунгицидтерді және инсектицидтерді пайдалану кезінде ауыл шаруашылығы өнімдерінің агроэкологиялық қауіпсіздігін есепке алу және бақылау;
- ғылыми-техникалық ақпарат пен арнайы әдебиеттерді, отандық және шетелдік аграрлық ғылымның жетістіктерін зерделеу;
- шаруашылық жүргізуші субъектілердің топырақтарына агрохимиялық мониторинг жүргізу және топыраққа, өсімдіктерге және тыңайтқыштарға химиялық талдау жүргізу;
- топырақ карталарын және агрохимиялық картограммаларды жасау;
- шаруашылық жүргізуші субъектілерде тыңайтқыштар мен мелиоранттарды қолдану тиімділігін экологиялық және экономикалық бағалау.
1.Бағалау: - ауылшаруашылық дақылдарын өсірудің заманауи агротехникалық әдістерін өндіріске енгізу және енгізу ретінде агрономның негізгі мазмұнын нақты көрсету негізінде:
- жер, су, орман, еңбек, материалдық және басқа да ресурстарды ұтымды және тиімді пайдалана білу;
- табиғатты қорғау, экологиялық қауіпсіз егіншілік жүйесін ұйымдастыру және әзірлеу, қауіпті зиянды заттардың болуына өсімдік шаруашылығы өнімдеріне сараптама жүргізу дағдыларына ие болу;
- өсімдік шаруашылығындағы технологиялық процестерді ұйымдастыра білу.
2. Конструктивтік: - шаруашылықтардың, жер және топырақ-климаттық ресурстардың мамандануын ескере отырып, фермерлік және басқа шаруашылықтар үшін заманауи қысқа мерзімді ауыспалы егіс схемаларын әзірлей білу;
- инновациялық технологиялар элементтерін енгізе отырып, ауыл шаруашылығы дақылдарын өсірудің технологиялық карталарын жасау;
- ауыл шаруашылығы машиналары мен жабдықтарын реттеуді жүргізу, Ауыл шаруашылығы дақылдарының тұқымын себу нормасын, тыңайтқыштарды, пестицидтерді, суару нормаларын және т. б. белгілеу;
- агроландшафттар және агроэкожүйелер;
- топырақ, олардың жұмыс істеу режимдері мен процестері;
- ауыл шаруашылығы алқаптары және ауыл шаруашылығы дақылдары;
3. Ақпараттық-технологиялық: - ауыл шаруашылығы дақылдарын өсіру технологиясын әзірлеу шеңберінде ауыл шаруашылығы дақылдарын өсірудің озық технологияларының әртүрлі көздерінен ақпарат жинауды, селекцияға қол жеткізуді, өсімдік шаруашылығындағы биотехнологияны, ГОСТ-тың өсімдік шаруашылығы өнімінің сапасына қойылатын талаптарын, өсімдік шаруашылығы өнімінің сапасын айқындау әдістерімен, өсімдік шаруашылығы өнімін сақтау және қайта өңдеу технологияларымен;
- шаруашылықтың бизнес жоспарын құра білу;
- топырақ құнарлылығын молайту және эрозиядан қорғау жөніндегі агротехникалық іс-шаралар жүйесін жоспарлау, ұйымдастыру және іске асыру;
- өрістердің фитосанитарлық жағдайын бағалау және дақылдардың зиянкестері мен ауруларының пайда болуын болжау;
- топырақ ресурстарын пайдаланудың оңтайлы тәсілін, жоғары экономикалық және экологиялық технологияларды химияландыру және механикаландыру құралдарын негіздеу;
- топырақтану мен агрохимияның қазіргі заманғы проблемаларын, топырақ құнарлылығын молайту технологияларын, экологиялық қауіпсіз өсімдік шаруашылығы өнімдерін өндіру саласындағы ғылыми-технологиялық саясатты білу.
- ауыл шаруашылығы дақылдарын өсірудің технологиялық карталарын жасау және оларға сәйкес дала жұмыстарын ұйымдастыру;
- ауыл шаруашылығы дақылдарының тұқымдарын, тыңайтқыштарды, пестицидтерді және т. б. себу нормасын белгілеу;
- мәдени жайылымдарды құру тәсілдерін және табиғи жемшөп алқаптарын ұтымды пайдалануды әзірлеу.